Video Real World Evidence - AS
Watch this 1-minute video to explore real-world persistence data in AxSpA patients treated with TNF inhibitors as collected by the RIC-France network.

RIC-France Network database
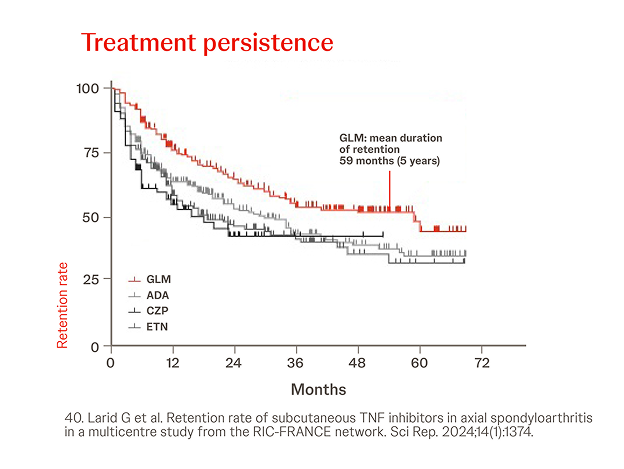
In a French multicenter retrospective observational study, 552 axSpA patients were included from 1081 records from a shared medical records database.
GLM had a significantly higher retention rate than ADA (p=0.002) , ETN (p<0.0001) and CZP (p=0.0001) in the overall population (all lines of treatment).40
Spanish biological drugs registry BIOBADASER
n = 294, year = 2021
In a retrospective analysis among 294 patients with axSpA treated with Simponi®, the probability of retention was higher when Simponi® was used as the first biological agent (log-rank p < 0.0001 for axSpA).33
.png?width=624&height=833&format=png&quality=50)

Australian national record claims registry
In a retrospective cohort analysis conducted using the Australian Commonwealth Department of Human Services Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme included data from 1,003 axSpA patients (n=275 on Simponi®). Persistence was significantly shorter with etanercept compared to Simponi�® in the second-line setting in patients with axSpA (HR 1.59, 95% CI 1.12–2.25, P=0.01). There were no other significant differences in persistence.39
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)
.png?width=624&height=833&format=png&quality=50)
OPAL dataset Australia
In a multicenter, retrospective noninterventional cohort study of 2,597 patients with AS treated in routine clinical practice in Australia was shown that when treatment persistence by first-line bDMARD was analyzed out to 150 months, patients on Simponi® displaying the longest median persistence.41

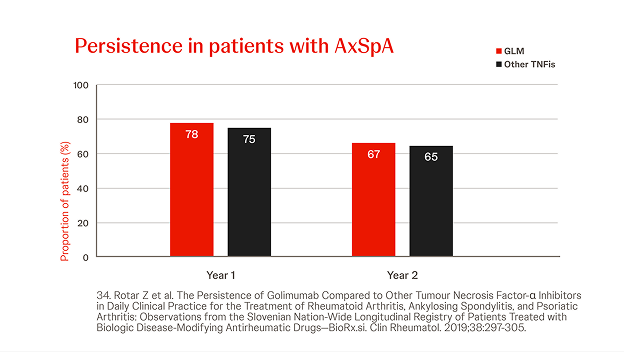
Slovenian BioRx.si registry
n = 2022, year = 2019
In a prospective analysis of axSpA patients treated with Simponi® (n=160) or other (n=452) TNFis (i.e. ADA, ETN, CZP, IFX), the persistence of Simponi® did not differ significantly at 2 years. Prior bDMARD exposure did not significantly influence the persistence of Simponi®, but was significantly lower for bDMARD-exposed patients in the other TNFi group.34
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)

Maccabi Health Service database analysis
n = 343, year = 2024
In a retrospective cohort study using computerized databases of Maccabi Health Services, adherence, persistence, and risk for discontinuation were assessed in 343 patients with axSpA (n=75 on Simponi®) and shown similar for all TNF-is and the IL-17i secukinumab, regardless of biologic-experience status.42
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)

RHADAR Network analysis on persistence between different MOAs
n = 1222, year = 2024
Retrospective analysis of the RHADAR database for axSpA patients with a new initiation of TNFi, IL17i or JAKi treatment in 1,222 patients. The 2-year persistence rates were 79.6%, 72.6%, and 62.8% for TNFi, IL-17i, and JAKi, respectively. The probability for discontinuation for JAKi was significantly higher compared with TNFi (HR 1.91 [95% CI 1.22–2.99]) as well as for IL-17i compared with TNFi (HR 1.43 [95% CI 1.02–2.01]), possibly related to more frequent use of TNFis as first-line therapy.44
.png?width=624&height=352&format=png&quality=50)
Abbreviations
ADA: adalimumab; AS: radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis; bDMARD: biological Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drug; CI: Confidence Interval; CZP: certolizumab pegol; ETN: etanercept; GLM: Simponi® (golimumab); HR: Hazard Ratio; IMRD: Immune Mediated Rheumatic Diseases; PsA: Psoriatic Arthritis; RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis; RCTs: Randomized Controlled Trials; RWE: Real-World Evidence; SC-TNFi: Subcutaneous Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitor; SOD: Survival on Drug; TNFi: Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitor.
References
23. Rotar Z et al. The Persistence of Golimumab Compared to Other Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Inhibitors in Daily Clinical Practice for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis: Observations from the Slovenian Nation-Wide Longitudinal Registry of Patients Treated with Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs—BioRx.si. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:297-305.
33. Pombo-Suarez M et al. Factors Associated with Long-Term Retention of Treatment with Golimumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Axial Spondyloarthritis, and Psoriatic Arthritis: An Analysis of the Spanish BIOBADASER Registry. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:3979-88.
39. Acar M et al. Treatment Persistence of Subcutaneous TNF Inhibitors Among Australian Patients with Immune-Mediated Rheumatic Disease (IMRD). Rheum Res Rev. 2018;10:151-60.
40. Larid G et al. Retention rate of subcutaneous TNF inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis in a multicentre study from the RIC-FRANCE network. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):1374.
41. Griffiths H et al. Persistence to biologic therapy among patients with ankylosing spondylitis: an observational study using the OPAL dataset. J Rheum. 2022;49:150-6.
42. Rosenberg V et al. Real-world adherence and drug survival of biologics among patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Clin Med. 2024;13:4480.
43. Strunz P et al. Analysis of the shorter drug survival times for Janus kinase inhibitors and interleukin-17 inhibitors compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in a real-world cohort of axial spondyloarthritis patients – a retrospective analysis from the RHADAR network. Rheumatol Int. 2024;44:2057-66.